Coffee beans are the cornerstone of one of the world’s most beloved beverages. These beans, the seeds of the Coffea plant, undergo various processes before gracing our cups with the aromatic and flavorful coffee. This article delves into the intricate composition of coffee beans, shedding light on the complex array of components that define their unique characteristics.
Key Takeaways
- Coffee beans contain a diverse range of chemical compounds that influence their flavor, aroma, and health benefits.
- Key components include acids, which contribute to the coffee’s acidity; alkaloids like caffeine, which provide stimulating effects; and phenols, responsible for bitterness and antioxidant properties.
- Other significant compounds are alcohols, amines, esters, ketones, organosulfuric compounds, and triglycerides, each playing a unique role in the bean’s profile.
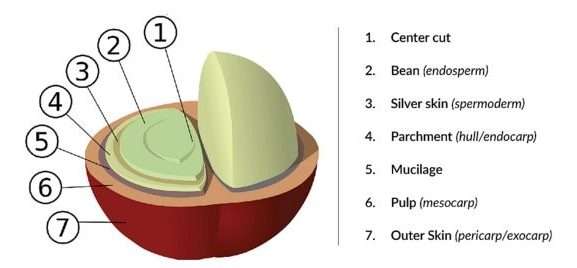
What is in Coffee Beans Composition
The term “green coffee bean” refers to the unroasted seeds, which are packed with compounds that evolve during the roasting process. These beans are not just a source of caffeine but also harbor numerous nonvolatile and volatile compounds that contribute to their overall sensory profile.
Green Coffee Beans and Their Components
Green coffee beans are a treasure trove of compounds, including caffeine, a well-known stimulant. But beyond caffeine, these beans contain nitrogenous compounds like trigonelline, which contribute to the coffee’s aroma and flavor when roasted. Carbohydrates in green beans also play a crucial role, influencing taste and the bean’s response to roasting.
Understanding the composition of coffee beans is essential for appreciating the beverage’s complexity and the factors influencing its taste and health benefits. Whether you’re a casual drinker or a coffee aficionado, recognizing these components enhances your coffee experience, connecting you to the intricate journey from bean to cup.
Chemical Compounds and Their Effects
Coffee beans are a mosaic of chemical compounds, each contributing to the beverage’s distinctive profile. Chlorogenic acid (CGA), a prominent component, is pivotal in shaping coffee’s flavor and health attributes. CGAs, prevalent in green coffee beans, influence the acidity and overall taste, altering perceptibly through roasting. They’re not only taste influencers but also recognized for their antioxidant properties, playing a role in mitigating oxidative stress.
Alkaloids like caffeine and theophylline are crucial for their physiological impacts. Caffeine, the most celebrated of these, is lauded for its stimulatory effects, enhancing alertness and concentration. On the other hand, theophylline, less abundant in coffee, shares similar properties but is primarily utilized in medicinal contexts for its bronchodilator effects. These compounds underscore the dual nature of coffee, acting as a sensory stimulant and a pharmacologically active substance.
The Impact of Brewing Methods on Coffee Composition
The brewing method is a critical determinant of coffee’s chemical narrative. Immersion methods, such as French press, allow coffee grounds to mingle extensively with water, extracting a robust flavor profile. In contrast, percolation techniques, like pour-over, offer a more controlled extraction, often resulting in a cleaner and more nuanced cup.
The interaction between water and coffee grounds during these processes can significantly alter the concentration of extracted compounds, influencing taste and aroma.
Water quality and grind size are pivotal in this chemical ballet. The mineral content in water can affect extraction rates and influence coffee’s flavor. Similarly, grind size dictates the surface area exposed to water, impacting the extraction efficiency of flavor compounds.
A finer grind increases the contact area, enhancing extraction but also risking over-extraction, which can lead to bitterness. These variables illustrate the intricate interplay of factors that define coffee’s final chemical makeup, offering insight into the precision required in brewing to achieve the desired cup profile.
Health Implications of Coffee Bean Composition
Coffee’s health implications are a blend of benefits and potential risks, largely influenced by its chemical makeup. Neurologically, coffee consumption is linked with reduced risks of Parkinson’s disease, attributed to caffeine’s neuroprotective properties. Studies suggest that caffeine may bolster dopamine levels, offering a shield against Parkinson’s.
However, coffee isn’t devoid of risks. Excessive intake can lead to insomnia, anxiety, and heart palpitations, highlighting the need for moderation. Understanding the balance between coffee’s beneficial antioxidants and stimulants like caffeine is crucial for leveraging its health advantages while minimizing risks.
FAQs
How does roasting affect coffee bean compounds?
Roasting transforms coffee beans, altering their chemical composition. It reduces chlorogenic acid levels but increases the formation of aromatic compounds, enhancing flavor while decreasing bitterness.
What’s the difference between arabica and robusta beans in chemical composition?
Arabica beans are typically richer in sugars and oils, contributing to their smoother taste, while robusta beans have higher caffeine content, offering a stronger, more bitter flavor.
Final Thoughts
The journey of understanding coffee bean composition unveils a fascinating intersection of chemistry, health, and gastronomy. Recognizing the nuanced dance of compounds within each bean not only enhances our appreciation of coffee but also informs our consumption choices.
As consumers and producers, delving into the bean’s inner workings can guide us towards more informed and enjoyable coffee experiences, marrying the art of brewing with the science of its constituents.









